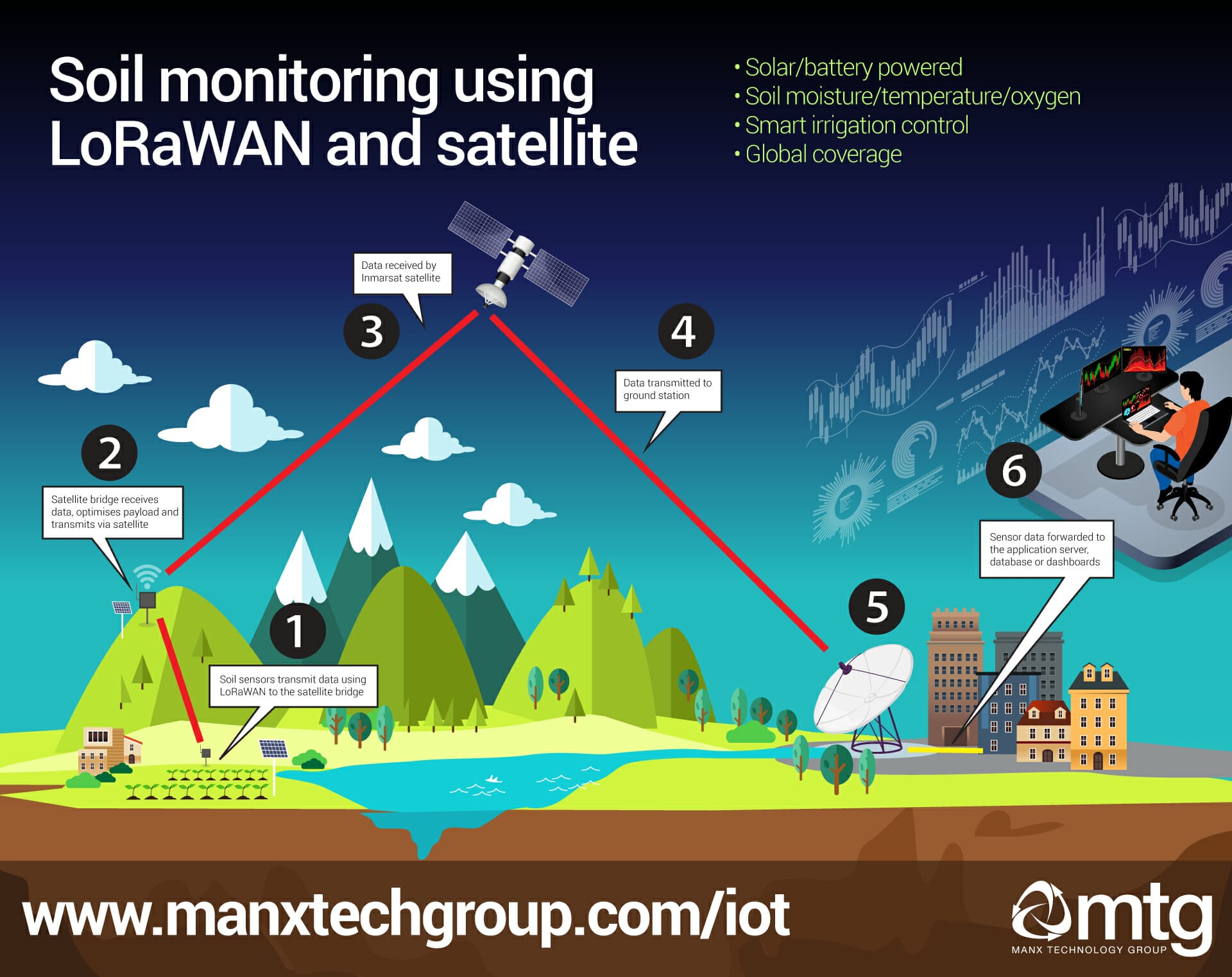
Soil Moisture, Temperature and Oxygen sensors, coupled with LoRaWAN satellite gateways, mean farmers can monitor soil conditions, even in the most remote regions. IoT technologies allow intelligent monitoring, precision agriculture and smart irrigation applications – without the constraints of power or mobile/internet coverage.
Remotely monitoring soil moisture and temperature are two popular applications of IoT technology. One challenge of agricultural deployments is farms are in remote, rural areas – often lacking the same infrastructure found in built-up urban areas.
LoRaWAN satellite gateways offer a solution that means farmers can use IoT sensors, even when traditional network coverage and mains power are lacking.
LoRaWAN soil sensors

IoT soil sensors can be used to monitor a variety of soil/weather metrics:
- Soil temperature
- Soil moisture
- Soil conductivity
- Soil oxygen levels
- Soil water potential
- Vapour pressure
- Solar radiation
- Surface temperature
The majority of sensors on the market use LoRaWAN networks that, as a general rule, can provide outdoor coverage of up to 15KM. Soil sensors can use battery or solar, meaning they can be deployed over several hundred acres, providing a good indication of soil health, or used for smart irrigation applications.
Despite the benefits and extensive coverage of LoRaWAN – this doesn’t solve the issue of getting data back to a cloud platform or central system.
Remote soil monitoring
Satellite connectivity has long provided a means to send and receive data all over the world using satellite. In many respects, LoRaWAN and satellite are the perfect pairings; both are perfect for telemetry or sensor data, both are suited to low data rates, and with the right choice of technologies – both can operate using solar panels.
Where remote soil monitoring is required, we would recommend using LoRaWAN sensors and a LoRaWAN satellite gateway.
The centralised gateway can provide connectivity for a sensor network up to 15KM from the base, while the satellite bridge can provide an uplink back to your central cloud platform. Best of all, all the systems will run on battery, solar, or combining the two.
Satellite coverage
The LoRaWAN satellite bridge can use both the Inmarsat and Iridium satellite networks – providing coverage throughout the entire world. The satellite gateway has an optimised protocol stack that minimises data transfer, keeping costs to a minimum – but providing a reliable platform for data transmission.
It is important to note that the bridge will also provide connectivity for a range of other IoT sensors, including weather stations, air quality, water quality and smart city sensors.
How much does remote soil monitoring cost?
There are three elements to a remote soil monitoring solution:
- Sensor cost (purchase) can be purchased as standalone sensors, with batteries and optional solar panels (depending on the vendor).
- Satellite bridge – the bridge is purchased, along with batteries or solar panels as required.
- Sensor cost (ongoing) – there is an ongoing charge for each sensor, covering license cost and data transfer costs.
Learn more
You can read more about soil monitoring in the following articles:
- Soil Monitoring with IoT – Smart Agriculture
- Internet of Things (IoT) Applications : Smart Agriculture : What, Why, How?
[sc name=”blogfooter” ]